- Home
- Social Action
- ★One Health Relay Report #19★
About "Viral zoonoses"

Profile #19: Dr. KARIWA Hiroaki, Professor
Laboratory of Public Health,
Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine
【Research Topics】
・Viral zoonoses
~Toward the Control of Viral Zoonoses~
In recent years, many zoonotic diseases have been occurring in various countries and regions around the world. The new coronavirus infection (COVID-19), which is now a major social problem due to its rapid spread throughout the world, is thought to have originated from a virus (SARS-CoV-2) that was originally carried by bats and somehow transmitted to humans, thus starting the current pandemic. Our laboratory focuses on viral zoonotic diseases such as hantavirus infection, tick-borne encephalitis, West Nile fever, severe febrile thrombocytopenia, and COVID-19. In particular, we are interested in elucidating the mode of viral persistence in the host* to prevent outbreaks of zoonotic diseases.
The following is an explanation of our research theme on hantavirus infections. Hantavirus infections are human infections caused by hantaviruses. Two disease types are known: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS), which is characterized by renal impairment and bleeding tendency, and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), which is characterized by respiratory impairment such as dyspnea. Although a wide variety of hantaviruses have been found in many animal species around the world, it has become clear that hantaviruses harbored by rodents are pathogenic to humans. We are currently conducting research on the replication patterns and host specificity of hantaviruses using rodent-derived viruses from Japan and overseas.
*Host: An animal species that is continuously infected with a pathogen in nature.
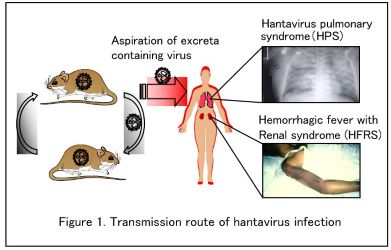

Transmission route of hantavirus infection. Setting traps for rodents.
Humans become infected by inhaling virus-containing excretions
from rodents and develop hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS)
and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS).
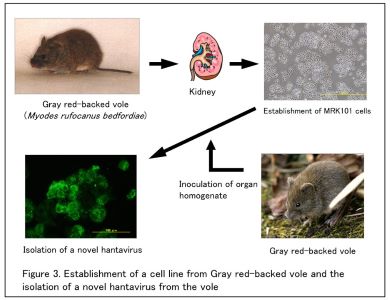
Establishment of a cell line from Gray red-backed vole
and the isolation of a novel hantavirus from the vole.
The isolation of the virus had been succeeded only by this cell line.
